Cells, Free Full-Text
Por um escritor misterioso
Descrição
Community-acquired pneumonia remains a major contributor to global communicable disease-mediated mortality. Neutrophils play a leading role in trying to contain bacterial lung infection, but they also drive detrimental pulmonary inflammation, when dysregulated. Here we aimed at understanding the role of microRNA-223 in orchestrating pulmonary inflammation during pneumococcal pneumonia. Serum microRNA-223 was measured in patients with pneumococcal pneumonia and in healthy subjects. Pulmonary inflammation in wild-type and microRNA-223-knockout mice was assessed in terms of disease course, histopathology, cellular recruitment and evaluation of inflammatory protein and gene signatures following pneumococcal infection. Low levels of serum microRNA-223 correlated with increased disease severity in pneumococcal pneumonia patients. Prolonged neutrophilic influx into the lungs and alveolar spaces was detected in pneumococci-infected microRNA-223-knockout mice, possibly accounting for aggravated histopathology and acute lung injury. Expression of microRNA-223 in wild-type mice was induced by pneumococcal infection in a time-dependent manner in whole lungs and lung neutrophils. Single-cell transcriptome analyses of murine lungs revealed a unique profile of antimicrobial and cellular maturation genes that are dysregulated in neutrophils lacking microRNA-223. Taken together, low levels of microRNA-223 in human pneumonia patient serum were associated with increased disease severity, whilst its absence provoked dysregulation of the neutrophil transcriptome in murine pneumococcal pneumonia.

A) Cell-free expression of sfGFP fused to a variety of N-and
Cells, Free Full-Text
Cancers, Free Full-Text

Label-free, full-field visualization of red blood cell (RBC)

Cells, Free Full-Text

Cell-free protein synthesis for producing 'difficult-to-express' proteins - ScienceDirect
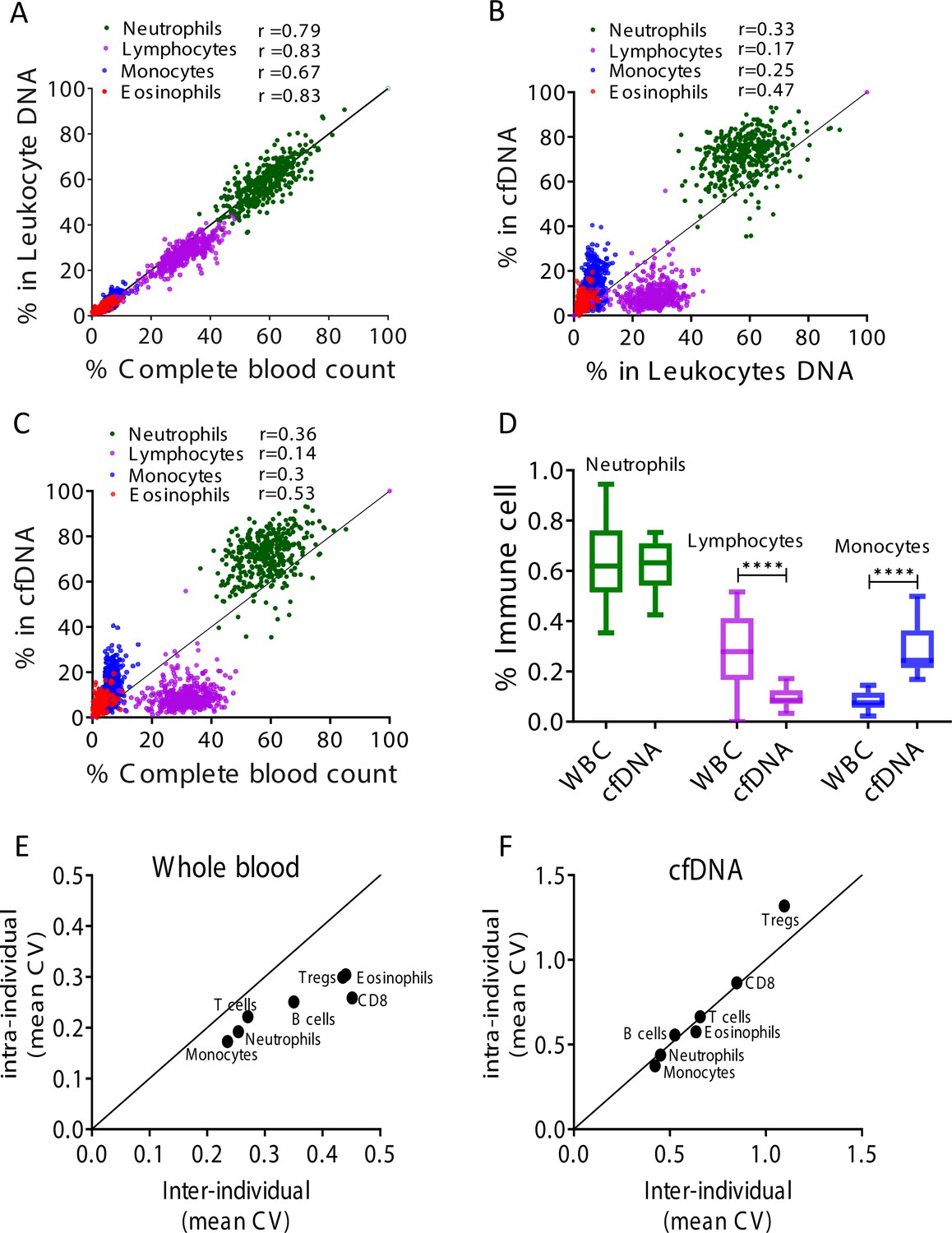
Remote immune processes revealed by immune-derived circulating cell-free DNA

Sequencing of Circulating Cell-free DNA during Pregnancy

Rapid cell-free characterization of multi-subunit CRISPR effectors and transposons - ScienceDirect
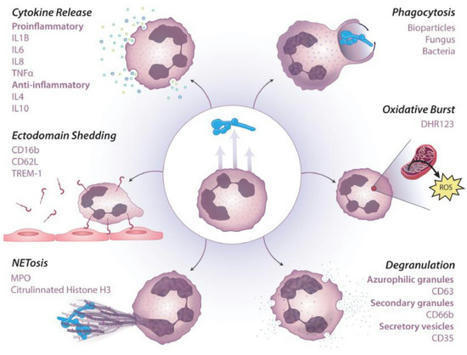
from Flow Cytometry to Cytomics, Page 2
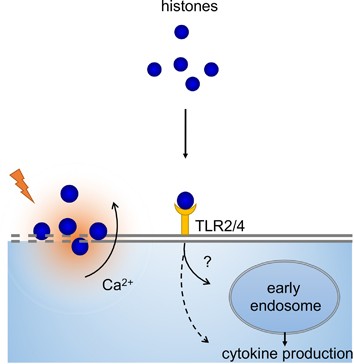
Extracellular histones, cell-free DNA, or nucleosomes: differences in immunostimulation
THE CELL : PAUL REVERE11 : Free Download, Borrow, and Streaming : Internet Archive
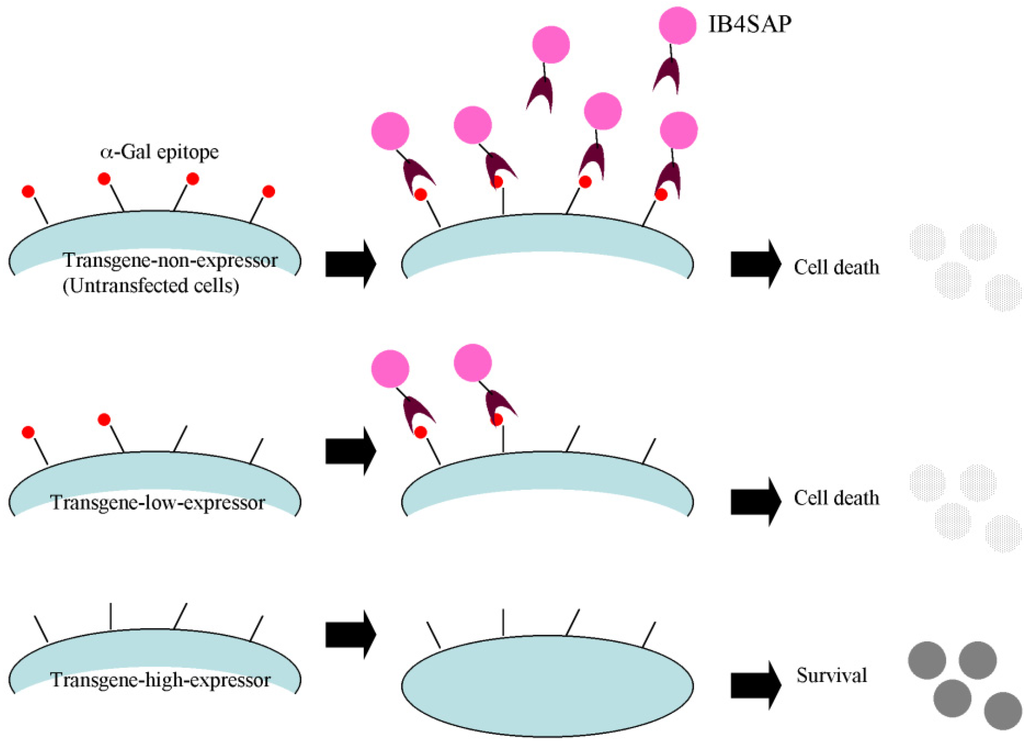
Biology, Free Full-Text

Cell-free mutant analysis combined with structure prediction of a lasso peptide biosynthetic protein B2

Cell-free biology: exploiting the interface between synthetic biology and synthetic chemistry - ScienceDirect
de
por adulto (o preço varia de acordo com o tamanho do grupo)